It used to take businesses decades to achieve a high valuation, but today some Silicon Valley startups achieve multi-billion dollar valuations (9 ZEROS!) in a matter of a few years. How is this possible? Which tools help entrepreneurs achieve such insane results in such a short period of time?
Spoiler Alert: Data visualization and data analysis is becoming increasingly important in the process of “blitzscaling” companies.
In this article we’ll take a look at how Elon Musk melds the “scientific method” with data science to drive the astronomical results of SpaceX – a private space company which currently outperforms the US, Chinese, and Russian space programs combined.
So, how did one man manage to beat the three most powerful world governments? Let’s suit up, take the elevator up to the catwalk and climb into SpaceX.
The Origins of SpaceX
SpaceX (also known as the Space Exploration Technologies Corp.) is the largest and most successful American-based aerospace manufacturer for space transportation and was founded by Elon Musk – a controversial entrepreneur and self proclaimed genius (and, currently, the richest man on the planet).
But its beginnings were not as bright as you might think…
Atmospheric Pressure After Launch
Elon Musk put $100 million of his personal fortune into this business and it nearly left him bankrupt as the first three launches led to brutal explosions. The press was all over the story even ridiculing Elon and his shattered and smoldering rockets. The company was on the verge of bankruptcy. Musk went on to say: ‘If the fourth launch hadn’t worked, that would have been it. We would not have had the resources to mount a fifth.’
Musk and his engineers didn’t give up though, and instead decided to use a strictly analytical approach and analyzed the failures that caused the first three rockets to blow up. Thanks to all of the data they had collected during those first launches and the post-launch investigation that they conducted, they knew what had gone wrong in each case: fuel leak (2006), stage separation issue (2007), residual thrust issue (2008). Equipped with all this information, they managed to drastically improve their rocket designs and the fourth launch was successful!
After the spectacular launch in 2008, SpaceX soon became a close collaborator of NASA, producing reusable rockets, shipping satellites into orbit and becoming something of a Space Uber transporting astronauts to the International Space Station. Since that first successful launch, the company has been on an upward trajectory and is now all over the world and across the galaxy.
The SpaceX Mission
Musk clearly states the mission of the company – he wants to send humans to Mars and set up a self-sustaining colony there. “Life would be boring if we had to stay on one planet forever”, he famously stated. Elon is never one to be shy with his opinion and on numerous occasions he openly shared his dissatisfaction related to the slow down of interplanetary space innovation.
In 1972, Apollo 17 was sent to the Moon, but since then humans have only traveled to the ISS (the International Space Station) which is in low orbit. In short: we’ve made no progress since 1972 (it could even be said that we’ve gone backwards).
Do you know how far away you live from the ISS, or even Mars?
Why is SpaceX so important?
One of SpaceX’s most significant contributions is the development of reusable rockets which drastically reduced the cost of space travel. This allowed them to put out more launches than any country in the world.
Here’s how SpaceX surged ahead of its competitors:
Elon’s hubris isn’t totally unfounded considering SpaceX is now launching more rockets than the rest of the world combined!
And here’s a price comparison between SpaceX Dragon 2 and other rockets:
SpaceX innovation has slashed the cost of manned space travel in recent years. Here’s how the historic rocket prices stack up.
SpaceX’s Secret Sauce(r)
So how did a small, new company manage to beat all the big players who were on the market for decades? Elon Musk highlights the importance of the “scientific method” which he applies not only to engineering problems, but to the entire business. He calls it “the algorithm” or “first principles thinking.”
That scientific, data-driven approach is what allowed SpaceX to succeed where all others failed before him. If not for a highly data-driven approach, they would not have revolutionized the entire industry.
SpaceX’s Manufacturing Hacks
While it might seem that manufacturing is straightforward, this is far from the truth. In fact, it’s a major bottleneck in many fields of engineering, including aerospace. So, what strategy has SpaceX adopted to manufacture their rockets so quickly and cheaply?
Elon Musk’s “First Principles” Methodology
Musk owes his success to his insane discipline and the problem-solving approach that he applies to each problem he encounters which he calls the first principles. This methodology involves breaking down complex problems into their most fundamental elements and then reassembling them from the ground up.
This method contrasts with reasoning by analogy, where solutions are based on what has been done before or on what others are doing. Musk encourages questioning and challenging assumptions and rethinking problems from a basic level to innovate and find more effective solutions.
In Walter Isaacson’s book about Musk, he mentions a story where all Musk’s friends are telling him that it’s impossible to build a reusable rocket. Elon’s response?:
“Does physics say it’s impossible? I can build a rocket for less than $100 million.”
Elon Musk
Cost Optimization
How did Elon Musk manage to build a rocket so much more cheaply than NASA and all the other big players?
On his trip to Russia, where he was supposed to purchase 2 rocket engines, he realized what all the rocket companies are doing wrong – they were purchasing different parts from different manufacturers, which makes the prices much more expensive while reducing the iteration speed of the engineering process.
SpaceX manufactures about 85% of its rocket components in-house. This approach allows the company to implement design changes quickly, drastically increasing the efficiency of production and reducing costs.
But not only that, the internal manufacturing approach ensures all components are ideally compatible with each other (making the product quality higher). Additionally, it eliminates the need for various “integration parts” previously required to combine elements from different suppliers which also had a drastic effect on the prices.
Now, the rocket production prices are ‘reasonable’ compared to what they used to be, but each launch is still extremely expensive. Thus, the next critical step in cost optimization is making sure that the probability of an expensive launch failure is as low as possible – and that’s where computer simulations come into play.
Advanced Aerospace Simulations
The Importance of Simulations
Aerospace projects, especially those involving space travel, are inherently high-stakes and expensive endeavors. Some launches can cost space companies more than a billion US dollars. Therefore, it’s crucial to take all the necessary steps to ensure that everything proceeds according to the plan before conducting actual physical tests or executing a final launch.
And that’s where the aerospace simulations come in. These computer simulations are becoming increasingly accurate and they quite often help detect unexpected issues with the design, drastically reducing the overall costs. A small design change needs to be tested? A minor bug has been fixed in the rocket’s software? You can run a new simulation and see what effect it has on the rocket.
How does SpaceX run its simulations?
SpaceX utilizes a variety of advanced software solutions to run its aerospace simulations and visualize predictions of what will happen. Each piece of software is related to a specific aspect of the spacecraft.
1. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Software – visualizes the flow of fluid (including air and fuel) within rocket engines and around the spacecraft
A screenshot of Autodesk CFD software:
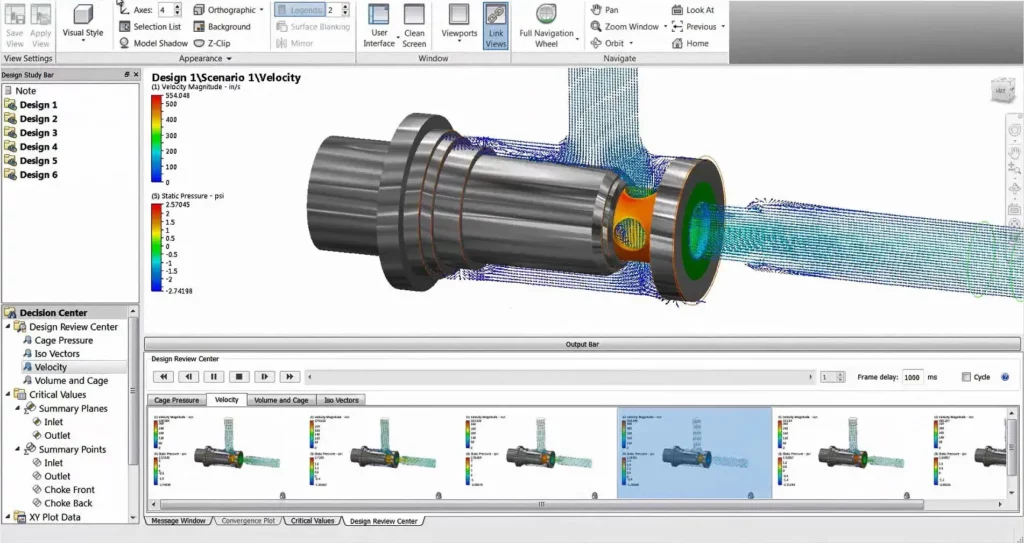
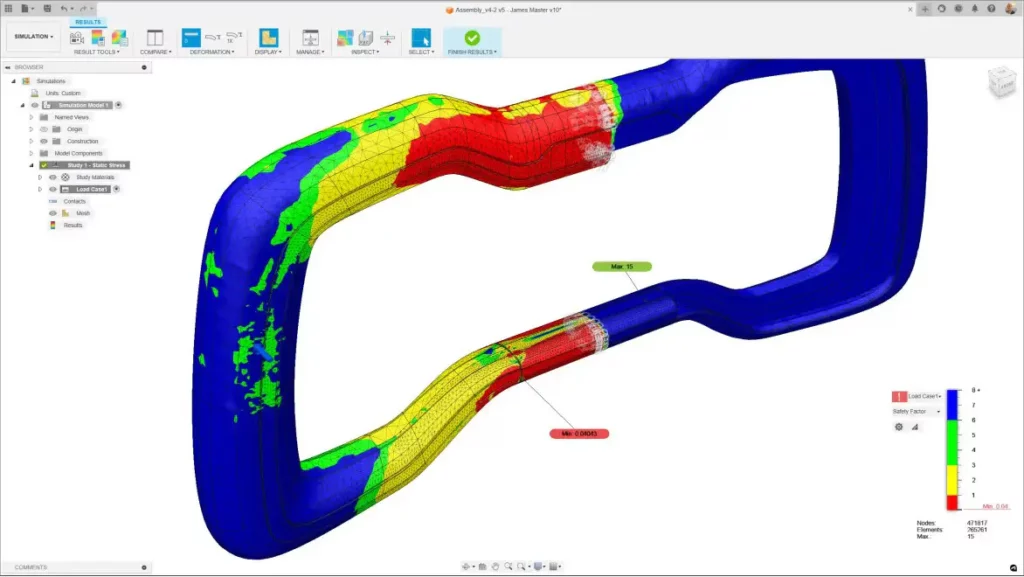
2. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Tools – for structural analysis (stress, thermal, vibration)
Screenshot of the FEA Autodesk software:
3. Computer Aided Design (CAD) Software – SpaceX uses SolidWorks, one of the most robust CAD software on the market to design parts for their spacecraft. With its material add-ons, SpaceX can visualize stresses and weak points on each part of the rocket, which is crucial for ensuring structural integrity.
Screenshot of an example rocket engine design from CAD software:
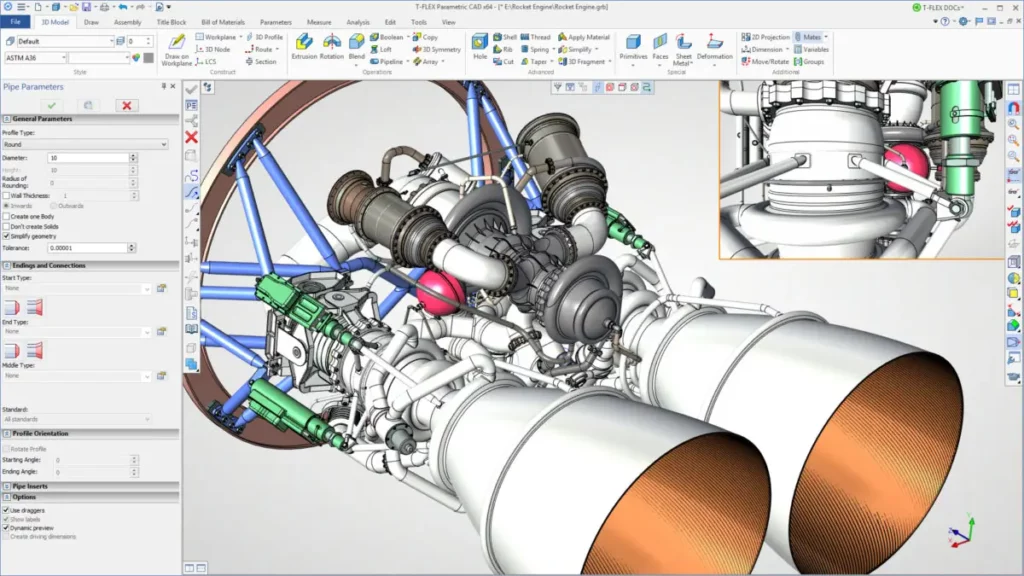
Pre-launch: data-based risk assessment
Before each launch, a comprehensive analysis of various environmental and weather-related factors is crucial. These factors significantly influence the trajectory and safety of a space mission.
What kind of data is needed before launch?
Every rocket company (SpaceX including) meticulously evaluates a range of meteorological and atmospheric data to ensure that the launch is safe.
Key factors that need to be considered:
- Temperature: Both ground-level and upper-atmosphere temperatures are assessed. Extreme temperatures can impact the rocket’s structural integrity and the performance of onboard instruments.
- Wind Speed and Direction: High winds, especially at higher altitudes, can cause the rocket to veer off course. Understanding wind patterns at various altitudes is crucial for plotting a safe trajectory.
- Humidity: High humidity levels can affect rocket systems and increase the risk of condensation and icing, which might lead to technical issues.
- Cloud Cover: Certain types of cloud formations, particularly those associated with thunderstorms, can be hazardous due to potential lightning strikes.
Analyzing those factors increases the probability that the launch will be successful – and math & statistics is all that matters in the scientific approach.
Time to Launch: Real-time Data Visualization
Musk says that every launch is a huge success, because even if it’s not successful, valuable data is gathered and they can learn from their mistakes and improve subsequent launches.
“Failure is an option here. If you aren’t failing at something, you’re not innovating.”
Elon Musk
The Importance of Gathering Data
The engineering process is an “iterative process” meaning that not everything will be perfect from the beginning, but the product or service will be constantly improved based on the gathered data.
SpaceX is no exception here – data plays an important role in its engineering process and without it rocket designs could not be improved.
What kind of data is collected?
During the launch, different sensors on a rocket gather & send data about telemetry:
- rocket’s position, velocity, and altitude
and environment (external conditions):
- temperature
- air pressure
- wind speed
Additionally, masses of engineering-related data is gathered, like:
- thrust levels
- fuel consumption
- engine temperature
- stress & strain on different parts
- flight path & trajectory data
This data is sent in real-time to the SpaceX computers, where they get a real-time visualization of all of those factors.
What happens when something goes wrong?
If the trajectory of the rocket is not perfect, it enters into a self-destruction protocol to prevent anyone on the ground from being harmed by a falling rocket. What would happen if there was no real-time communication between the rocket and the SpaceX engineers? Hurt humans and no data to learn from = repeating mistakes from the past.
Fortunately, loads of data is gathered and the company is able to develop new technologies to address any issues in a timely manner. With this rapid pace of progress, SpaceX is now not only building rockets, but sending thousands of satellites into orbit, providing us with internet access in areas where there used to be no signal. How does it work?
Starlink – the global internet
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation constructed by SpaceX which aims to provide high-speed internet access across the globe.
“There’s no signal!” – the importance of Starlink
The phrase “there’s no signal” is obsolete when it comes to Starlink. Satellite-based communication allows high-speed internet access all around the globe.
This global coverage has significant positive impacts, especially for underprivileged regions, as it opens up internet access to populations in poorer countries.
However, the influence of Starlink extends beyond just providing internet access. As a relatively new venture of SpaceX, Starlink has already become a notable player in international affairs, notably impacting the dynamics of the conflict between Russia and Ukraine.
Starlink coverage
There’s a lot of data analysis involved in Starlink – before taking a satellite into orbit, we need to take into account its lifetime, velocity, frequency and bandwidth allocation (in order to prevent wave interference).
Starlink engineers have been very successful in the analysis of those factors, testament to which is the huge increase in Starlink coverage.
This, again, would not be possible without a thorough analysis of all different variables.
Give the globe a spin and discover where Starlink satellites are currently available.
Mission Recap
We covered a lot of ground, or space rather, so let’s recap:
- Data visualization plays a crucial role in SpaceX’s innovation and success in the aerospace industry.
- Elon’s emphasis on data-driven decisions and the “scientific method” revolutionized rocket design, making space travel more cost-effective.
- SpaceX’s utilization of advanced simulations and real-time data visualization during launches helped make more accurate predictions about their launches.
Through Musk’s visionary approach and a dedication to leveraging data, SpaceX has emerged as a leader in space exploration and commercial spaceflight, setting new benchmarks for efficiency and reliability in the sector.
This is certainly not the end of the story for SpaceX but rather just the beginning. Even though Elon Musk is focusing some of his attention on new data-centric ventures including X (previously Twitter), Grok, and xAI, his dedication to SpaceX remains steadfast.
To the future and beyond!
The Future of Dataviz
Speaking of the future, with the advent of generative AI, GPT-4 and Gemini, the future of data visualization is bright indeed. Data is the lifeblood of business, culture, entertainment these days and good dataviz helps everything run smoother and makes it easier for users, regardless of their job title, to see patterns and make decisions. That’s why jobs in data visualization and analysis are really taking off.
As a crew member of the starship Black Label, I’m excited to help clients discover new dataviz technologies and solutions. Watch this Space!












